The Nucleic Acid of a Virus Particle Is Enclosed
A full understanding of how the nucleic acid molecule contributes to increase the stiffness of the MVM particle would require a complete structural description of the enclosed nucleic acid. A virus particle consists of one or more strands of nucleic acid DN A or RNA enclosed in a protein shell called a capsid.
Nucleic acid genome surrounded by a protein coat capsid additionally surrounded by a membrane envelope There are all sorts of virus shapes and sizes.

. Complete virus particle consists of 1 molecule of DNA or RNA enclosed in coat of protein may have additional layers. Viral nucleic acid enclosed by a capsid protein coat Envelopesyn. Viral capsids ensure viral genome integrity by protecting the enclosed nucleic acids.
Is merely a means of making new virus particles. A protein coat that covers the nucleoprotein core or nucleic acid RNA DNA of a free virus particle or phage which may have icosahedral symmetry and itself be enclosed in an envelopeeg Togaviridae. 63 Viral multiplication 1.
It is generally inside the cytoplasm. The nucleic acid of a virus particle is enclosed in a protein coat. A virus is a very small infectious particle consisting of nucleic acid enclosed in a protein coat and in some cases a membranous envelope.
Nucleocapsid alone for some viruses picornaviruses or including outer envelope structure for others retroviruses. Some viruses also have an outer envelope composed of fatty materials lipids and proteins. Viruses are tiny organisms that contain nucleic acid encased by a protein coat.
7 What does the core of every virus particle always contain. Viruses are extremely small approximately 15 - 25 Scientists have long sought to uncover the structure and function of viruses. 5 How does a virus differ from a bacterium.
Viral genomes may consist of either. The nucleocapsid Protein N-protein is the most abundant protein in coronavirus. Viruses are very small infectious particles consisting of nucleic acid enclosed in a protein coat and in some cases a membranous envelope 封套.
Up to 24 cash back A virus particle also known as a virion is essentially a nucleic acid DNA or RNA enclosed in a protein shell or coat. Several copies of the complete viral genome may be enclosed within a single virion or virions may be formed that contain no nucleic acid empty particles or that have an incomplete genome defective particles and in some cases defective interfering particles by virtue of modulating replication. A simple sketch of a virus.
Therefore assembly of the complete particle always involves. 9 What part of the virus determines which host the virus infects. See Concept 191 Page 397.
This organisms cannot grow reproduce or carry out their functions without a host cell. The N-protein is a highly immunogenic. 8 Is the protein shell around the nucleic acid core of a virus.
Further when this virion particle infects the host cell it replicates to form virus particles inside the infected host. Textbook solution for Prescotts Microbiology 10th Edition Joanne Willey Chapter 386 Problem 1RIA. Some are enclosed by an envelope of fat and protein molecules.
The nucleic acid of a virus together with the protein coat that encloses it. 10 How do viruses differ from. 6 What is the difference between DNA virus replication and RNA virus replication.
The capsid helps in providing specificity to the virus and the core provides infectivity. Depending on the virus the nucleocapsid may correspond to a naked core or be surrounded by a membranous envelope. Moreover host cell DNA may sometimes be incorporated into.
A virus is a very small infectious particle consisting of nucleic acid enclosed in a protein coat and in some cases a membranous envelope. Double- or single-stranded DNA or Double- or single-stranded RNA Depending on its type of nucleic acid a virus is called a DNA virus or an RNA virus. Multipartite is a class of virus that have segmented nucleic acid genomes with each segment of the genome enclosed in a separate viral particle.
Interactions between the genome and capsid and between individual capsid proteins ie capsid architecture are intimate and are expected to be characterized by. A virus consists of a single- or double-stranded nucleic acid and at least one protein surrounded by a protein shell called a capsid. A virus invades living cells and uses their chemical properties in order to keep itself alive and reproduce.
Published by Houghton Mifflin Company. Viruses are not cells. This protein coat is called a capsid and the instructions for.
The length of the nucleic acid also varies from virus to virus Genomes can be segmented or circular 19. In many viruses the capsid it self is enclosed in a membrane with pro tein molecules embedded in it much like the outer membrane of an animal cell. Describe the five steps common to the life cycles of all.
Only a few ssDNA viruses have multipartite genomes but a lot more RNA viruses have multipartite genomes. Bacteriophage fd is a class I filamentous virus others are M13 and f1 that comprises a circular single-stranded DNA molecule enclosed in a cylindrical protein sheath to form a flexible particle approximately 890 nm long and 7 nm in diameter. In the simpler viruses the virion consists of a single molecule of nucleic acid surrounded by a protein coat the capsid.
Nucleocapsid is an unit of vrial structure consisting of a capsid with the enclosed nucleic acid. What is it called. In all virus particles the nucleic acid genome is enclosed in a particle consisting largely of virus-coded protein subunits.
Depending on its type of nucleic acid a virus is called a DNA virus or an RNA virus The genome is either a single linear or circular molecule of the. It is composed of an integer multiple of 60 subunits which self-assemble in a pattern typical for a particular virus. An outer protein shell called a capsid An inner core is of nucleic acid.
The American Heritage Medical Dictionary Copyright 2007 2004 by Houghton Mifflin Company. The viral DNA contains 6408 nucleotides incorporating 10 genes and the protein sheath is composed of about 2700 major. This description is still unavailable for any icosahedral virus because most of the viral nucleic acid molecule is asymmetrically arranged inside the.
However all virus particles have a protein coat that surrounds and protects a nucleic acid genome. An advantage of multipartite genome is its ability to synthesize multiple mRNA strands to avoid the cellular. A virus is an infectious particle consisting of.
We have step-by-step solutions for your textbooks written by Bartleby experts. Regular shell-like structure composed of aggregated protein subunits which surrounds the viral nucleic acid Nucleocapsid syn. A virion is an entire virus particle that consists of two shells.
The capsid and its enclosed nucleic acid together constitute the nucleocapsid.

Virus Particle An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
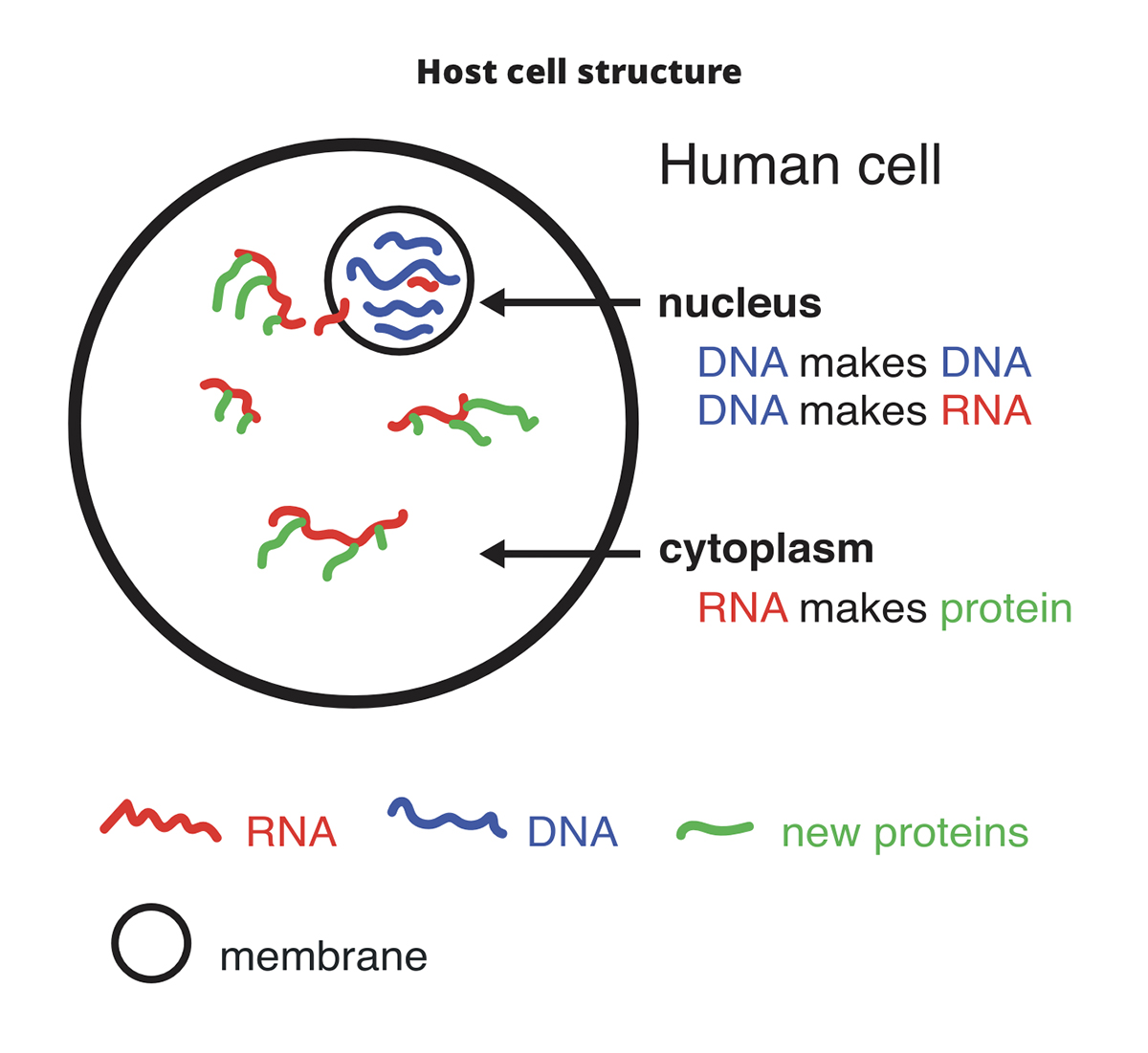
What Is A Virus An Exploration For Middle School Students

Virus The Cycle Of Infection Britannica
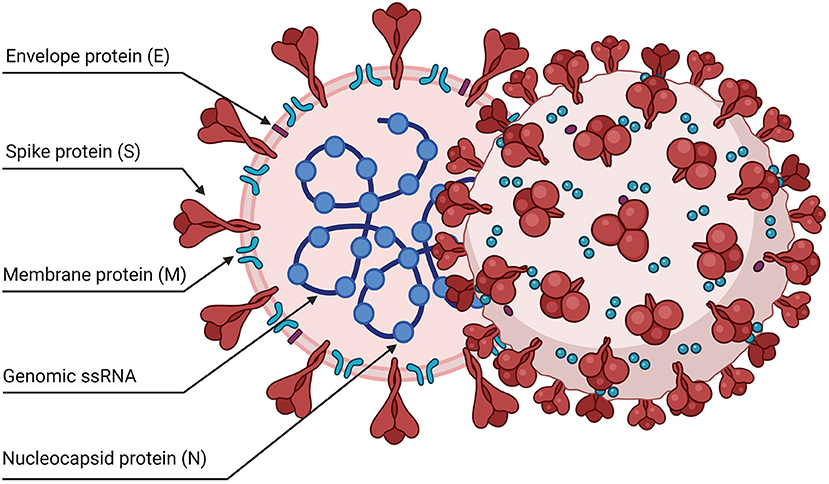
Frontiers Sars Cov 2 And The Host Cell A Tale Of Interactions Virology
Physics Of Viral Dynamics Nature Reviews Physics
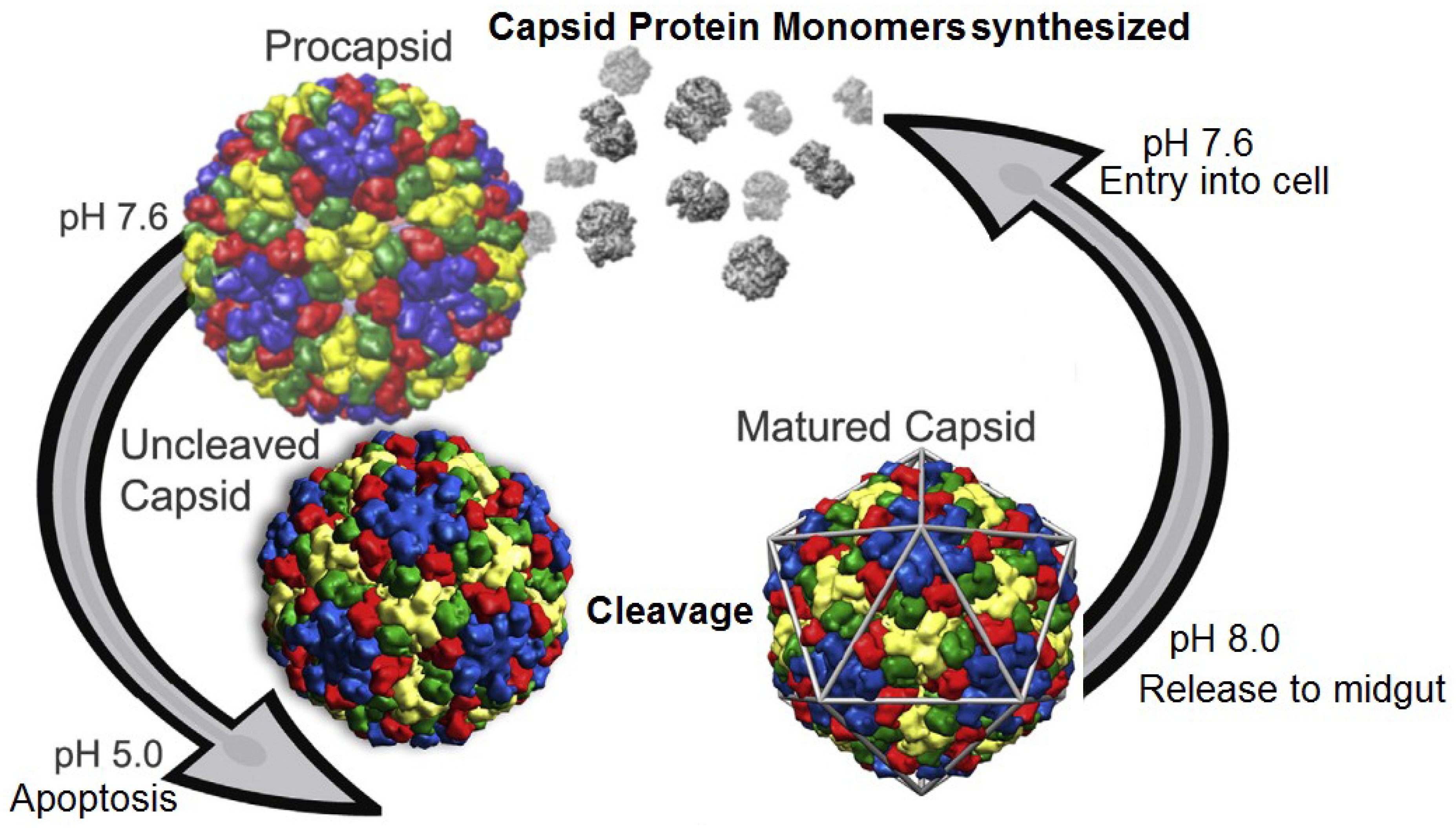
Viruses Free Full Text Assembly And Maturation Of A T 4 Quasi Equivalent Virus Is Guided By Electrostatic And Mechanical Forces Html

Capsid An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Viruses Artificial Viruses And Virus Based Structures For Biomedical Applications Van Rijn 2016 Advanced Healthcare Materials Wiley Online Library

Virus Evolution Of New Virus Strains Britannica

Virus The Cycle Of Infection Britannica

Virus The Cycle Of Infection Britannica
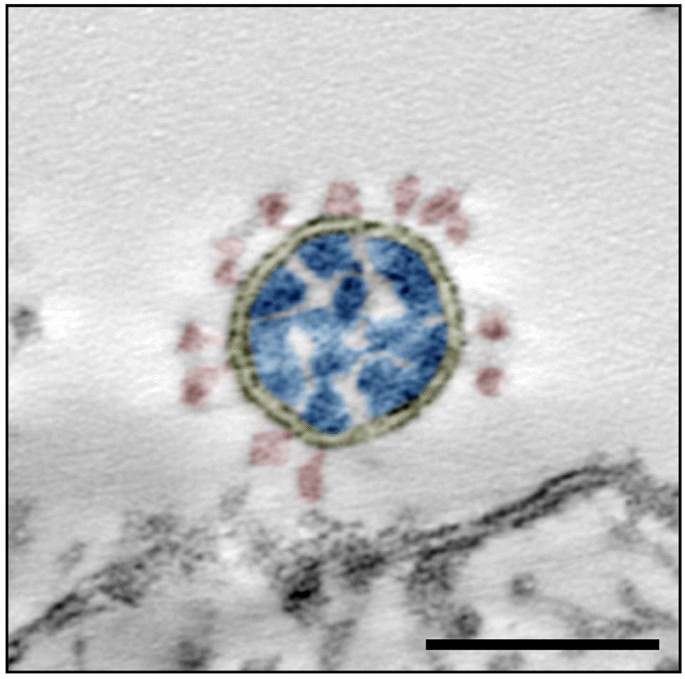
Morphometry Of Sars Cov And Sars Cov 2 Particles In Ultrathin Plastic Sections Of Infected Vero Cell Cultures Scientific Reports
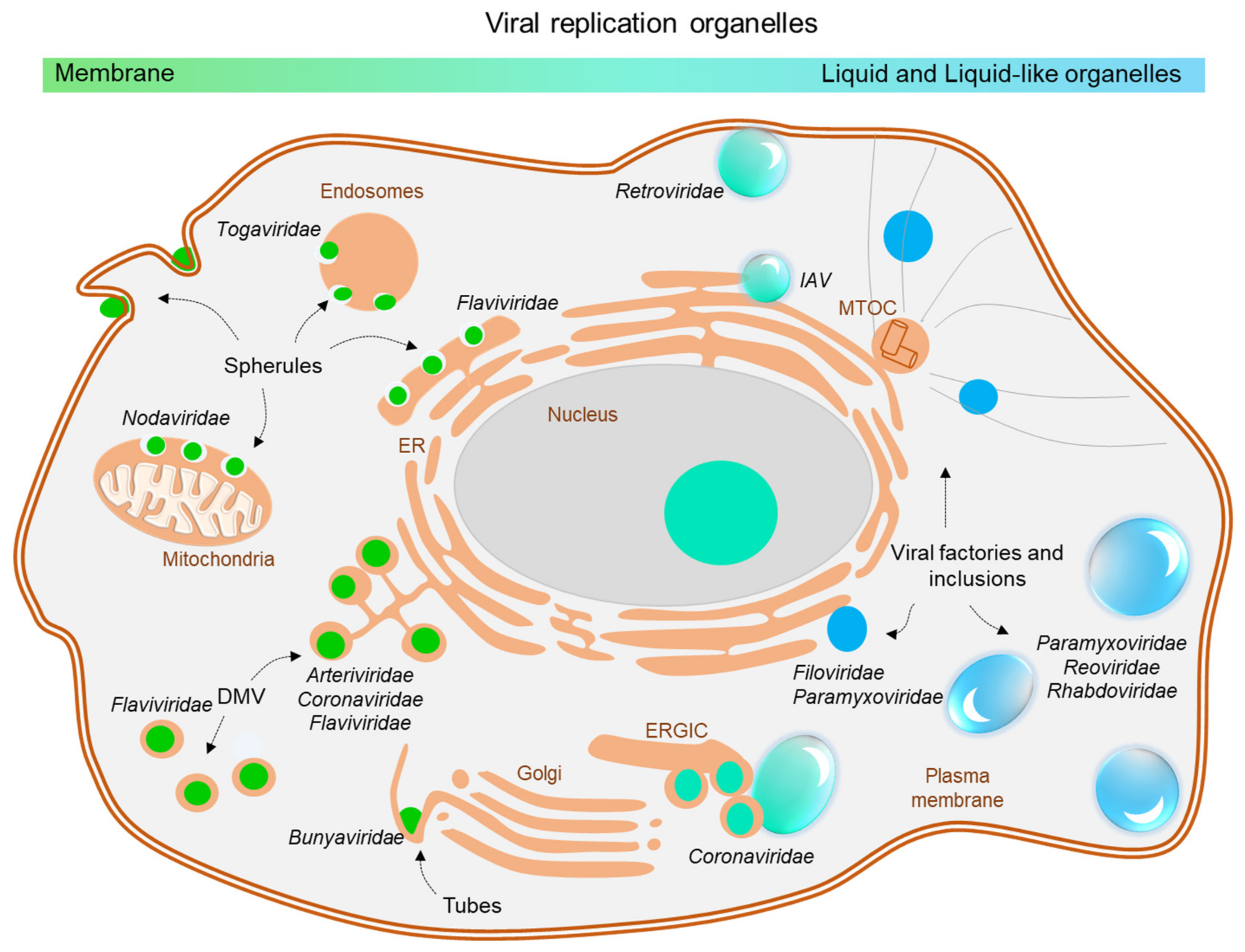
Cells Free Full Text New Perspectives On The Biogenesis Of Viral Inclusion Bodies In Negative Sense Rna Virus Infections Html
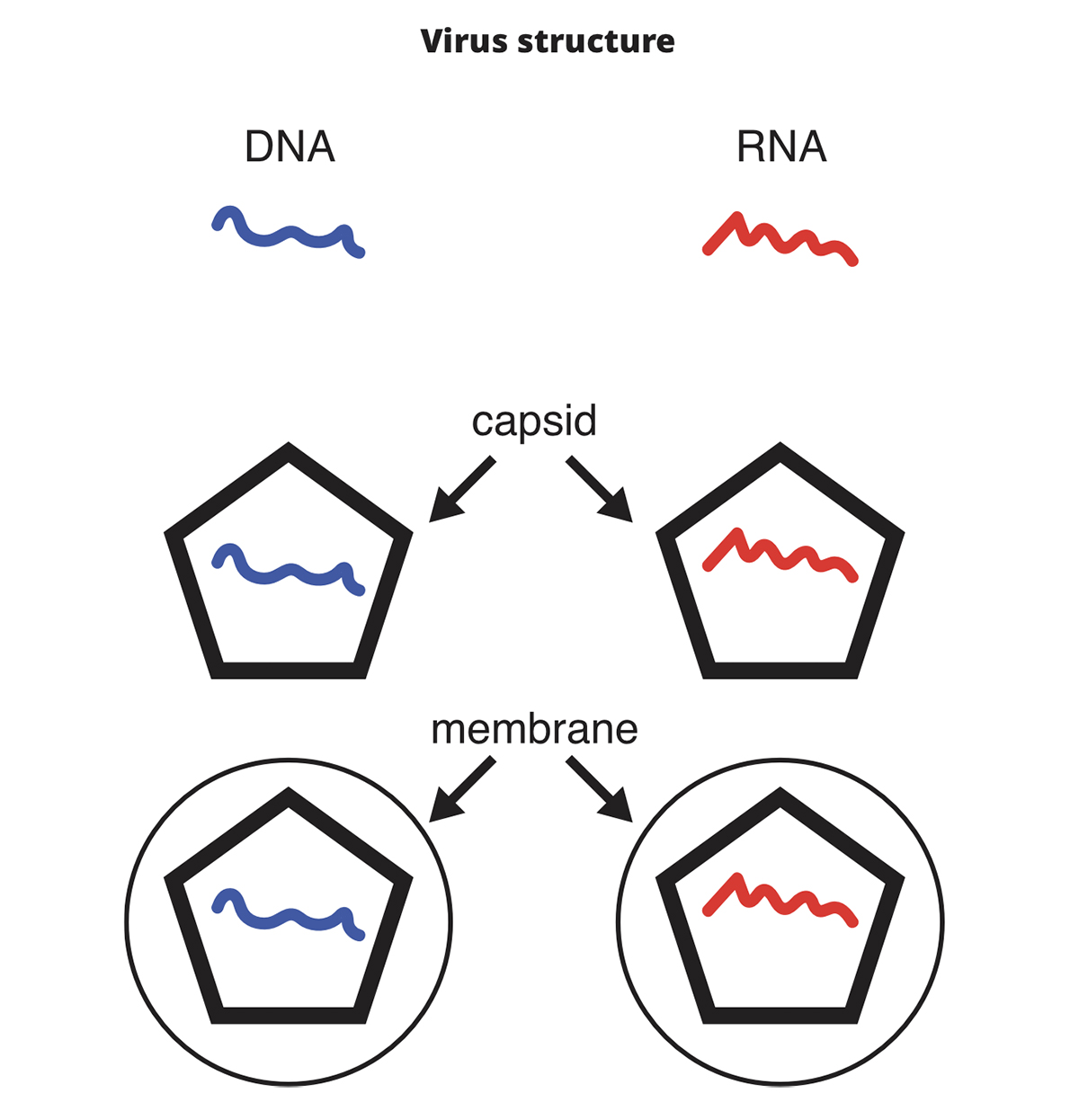
What Is A Virus An Exploration For Middle School Students

Schematic Diagram Of Coronavirus Particle The 26 32 Kb Long Viral Download Scientific Diagram

Schematic Depictions Of Key Structural Features In A Influenza A And Download Scientific Diagram
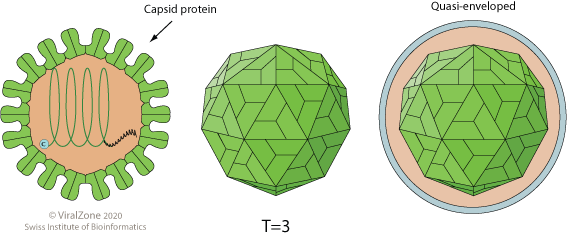

Comments
Post a Comment